Venture Capital – Financing the Dreams of Startups
Venture capital means the financial capital supplied to the early stage & high potential growth startup companies. A VC fund earns the money by owning the equity in the company in which it is investing. Mostly, they have some novel technology or a business model in the high technology industries such as biotechnology & IT. The typical VC investments occur to get a return through the eventual realization events such as the trade sale of company or an Initial Public Offering. It is also called as the Series ‘A’ round. VC is a form of private equity.
In addition to the equity crowd funding, angel investing & other seed funding options, VC is much attractive for the newer companies with a limited operating history which are much smaller to raise the capital in public markets & which haven’t reached to the point where they can complete the debt offering or secure a loan from the bank. In the exchange of the high risk which venture capitalists take by investing in the smaller & the less mature companies, they get a significant control over the company decisions as well as a substantial portion of the ownership of company & consequently monetary value of it.

image:pixabay
VC is also associated with the job creation which accounts for the 2% of the GDP in US, the knowledge economy & is used as a measure of the innovation in an economy or geography. From the statistics, it can be seen that nearly 2 million new businesses are created in the US every year & around 800 get VC funding. According to NVCA, 11% of the total private sector jobs are from the venture backed companies & venture backed revenue accounts for almost 21% of the GDP of the country.
It is also a way in which both the public & the private sector can construct an institution which systematically creates the networks for the progress of the new industries & the firms. This institution helps in the identifying & combining the pieces of the companies such as business models, marketing knowhow, technical expertise & finance. Once these enterprises are integrated, they succeed by becoming the nodes in search networks to design & build the products in their domain.
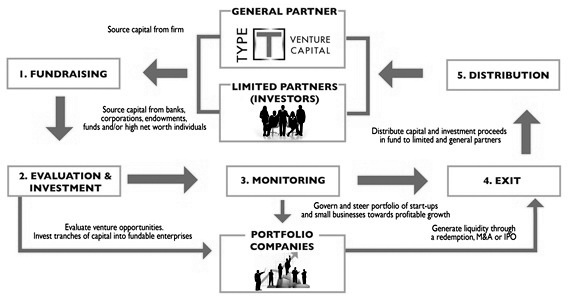
Obtaining a VC is significantly different from that of raising a loan or a debt. Lenders do have a legal right to charge an interest on the loan & to ensure the repayment of capital no matter if venture is a failure or a success. VC is invested for the exchange of an equity stake in the company. The return on the investment for the venture capitalist as a shareholder hinges on the profitability & the growth of the business. This return is earned when venture capitalist exits the business by selling his shares when the business is sold to the some other owner.
Generally, those venture capitalists are very selective in deciding about what to invest in. As a result, the firms are looking for the extreme qualities such as potential for the rapid growth, innovative technologies, an impressive management team & a well-developed business model. Among all these, funds are most interested in the projects with an exceptionally high growth potential. Since such ventures most likely provide the financial returns & a successful exit in the expected time frame by venture capitalists. The time frame typically varies between 3 to 7 years.
The investments are not liquid & it also need an extended time frame for harvesting. So the venture capitalists are expected to carry out the detailed due diligence before the investment & nurture the company in which they are investing, to increase the likelihood of reaching to an initial public offering stage when the valuation of the project is favorable for the venture capitalists.
Since there are not any public exchanges listing their securities, the private companies meet the VC firms & other private equity investors in some of the ways which include referrals from the trusted sources of the investors or other business contacts, investor symposia & conferences as well as the summits where the companies directly pitch to the investor groups in face to face meetings. It also includes Speed Venturing. It is akin to speed dating for capital. In this case, within 10 minutes, an investor decides if he is interested in the idea & wants a follow up meeting. Also, many new private online networks are coming into business. They provide an additional opportunity to meet the investors.
This need for the high returns makes the venture funding an expensive source of capital for the companies & most suitable for the businesses which have the large up front capital requirements that can’t be financed by some other cheaper alternatives like debt. This is a very common case for the intangible assets like software & other intellectual properties whose value cannot be proved. So, In turn, it explains why the VC is most prevalent in the fast growing technology & biotechnology fields.
If a company has the qualities the venture capitalists seek including a good management team, a solid business plan, target minimum returns of 40% per year, a good potential to exit the investment before an end of their funding cycle and the investment & passion of the founders, the company will find it much easier to raise the capital.
Mainly, there are 6 stages of the venture round financing. They correspond to the following stages of the development of a company.
• Seed funding - it is the first round of financing needed for proving a new idea, generally provided by angel investors. Another emerging option of the seed funding is equity crowd-funding.
• Startup – The early stage firms which need the funding for the expenses associated with product development & marketing.
• Growth - They are early sales & manufacturing funds. This is where the Venture capitalists come in. This series A round can be thought of as the first institutional round.
• Second Round - Working capital for the early stage companies whose products are being sold but the companies are yet to make a profit. This is the subsequent investment round to series A & hence can be called as Series B round. The next one is series C & so on.
• Expansion - This is the money for the expansion of a newly profitable company. It is also called as the mezzanine financing.
• Exit of the venture capitalist- Venture Capitalists can exit from the company through an acquisition, the secondary sale or an initial public offering. Early stage Venture Capitalists may exit in later rounds when the new investors either Venture Capitalists or the private equity investors buy the existing shares of or an investor a venture capitalist. Sometimes, a company which is very close to an initial public offering may allow some of the venture capitalists to exit the business & instead, new investors can come in the hope to earn the profit from the initial public offering.
• Bridge Financing – It comes when a startup seeks funding in between full venture capitalist rounds. The objective of bridge financing is to raise the smaller amounts of money instead of a full round. Here, the participants are mostly existing investors themselves.
This article has been authored by Gopal Zavar from SIMSR
Views expressed in the article are personal. The articles are for educational & academic purpose only, and have been uploaded by the MBA Skool Team.
If you are interested in writing articles for us, Submit Here
Share this Page on:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
All Business Sections
Write for Us