Voice over Internet Protocol - VoIP - Definition & Meaning
What is Voice over Internet Protocol - VoIP?
Voice over Internet Protocol VoIP is a procedure for the transfer and transmission of voice communications and multimedia sessions over Internet Protocol (IP) networks, such as the Internet. It is a technology that allows telephone calls to be made over the internet.
VoIP converts analog voice signals into digital data packets and supports real-time, two-way communication of conversations over the internet. Users in most cases are also able to see each other.
VoIP calls can be made on the Internet using a VoIP service provider (network provider) and standard computer audio systems. However, ordinary telephones with special adapters might also be used to connect home networks.
Most VoIP implementations are based on the H.323 technology standard.
Advantages
• VoIP offers cheaper long distance telephone calls.
• VoIP allows video conferencing to be done over long distance networks, connecting two people in two different parts of the world.
Disadvantage
• The main disadvantage of VoIP is a greater possibility for dropped calls and degraded voice quality when the network is heavily loaded.
Examples:- Skype, Teamspeak and Ventrilo.
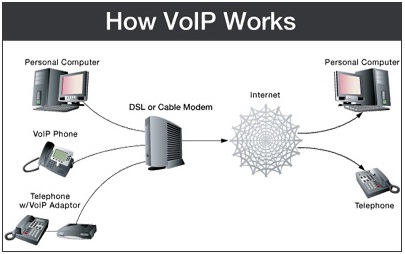
Illustration (How VoIP works)
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us