Retailer - Definition, Importance, Types & Example
What is Retailer?
Retailer is the one who sells goods/services directly to consumers for their personal or non-business use. Retailers are business entities which act as an intermediary between producer & consumer of goods. Retailer purchase goods/services from wholesaler or distributor and sells to end customers at marked-up prices. They are intermediaries between consumer and wholesalers (or manufacturers).
Importance of Retailer
Retailers play an indispensable role in creating a market for a product or promoting a product because they are the one who can influence consumer purchasing behavior. They purchase products from manufacturers or from wholesalers, who keep the products in warehouses as storage.
They have huge shops, supermarkets etc. where they organize all the different type of products which are available for customers to buy.
End consumers can directly come to such retail outlets and purchase these goods.
Roles of Retailers in Business
Retailers play one of the most important role in the business and cater to the end customers helping the supply chain and demand/supply cycles.
Some of the important roles performed by retailers are:
1. Purchasing and Stocking
They need to purchase different variety of goods depending on the customer base and needs to stock them safely before selling. End customers will prefer goods which are in good condition and are fresh. Also customers prefer stores where they can experience or see the product well before buying.
Retailer has to make sure of the final quality.
2. Influencing consumers and Selling
They are the one whom consumers believe and hence has the ability to convince consumers to purchase the particular goods and sells the same. Activities like upsell, cross sell and final sales promotion is many times handled by the end retailers in partnership with companies and brands.
They also need to be aware of the value proposition being offered so that the same can be communicated to the end customer.
3. Assumption of Risk
They need to take several risks like- the risk of storing goods which may deteriorate, risk of change in fashion and hence in consumer buying behavior etc. Retailer being the last player in the supply chain has to assume these risks. Sometimes after stocking a product, there may be recall or some defect which increases the loss or administrative tasks for the retailer.
4. Calibrating and Packing
Based upon consumer needs, retailers need to calibrate, pack and sell products accordingly. Many a times, retailer has to be the part of the final packaging in case of products which are sold by quantity.
E.g. fruits based on dozens or wheat based on weight. Retailer needs to make sure that the right quantity is delivered to the customer along with the right packaging.
5. Giving credit
They give goods to consumers on credit basis in order to get hold of consumer for longer time. Retailers help businesses and customers by acting as a line of credit in their influence areas.
E.g. Convenience stores can help the customers by giving them monthly credit for delivering essential items.
6. Taking customer’s feedback
Retailers are the one who directly interact with end users and hence are in the position to provide genuine feedback to the manufacturer regarding products and its services.
Many manufacturers and service provides depend on retailers for the actual customer feedback and sales data to improve the offerings.
7. Advertising
If retailers are given additional discounts in certain products, then they push those products by advertising and releasing certain schemes themselves. Many a times we see hoardings at the retailer promoting a particular product.
6 Types of Retailers
There are multiple types of retailers based on the service and range of products they offer:
1. Departmental Store
Department stores have been in the retail since long time. Departmental stores as retailers have large amount of product variety and cater to a large number of customers on a daily basis. Departmental store can be a one big retailer or a group of many small retailers in one area
2. Supermarkets
Supermarkets are similar to departmental stores but differ in terms of influence and budget. They also stock large number of products and brands but are more structured in operations and retail.
3. Warehouse Retailer
Located in areas with low rent and stocks a large amount of products at one place but offers more discounts and lower prices as compared to departmental stores and supermarkets.
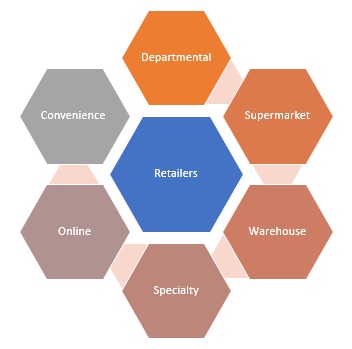
4. Specialty Retailer
There are kind of priority dealers who have nice products or brands from a single company like Samsung store or Apple iStore.
This retailer provides more options and better service as compared to other retailers.
5. Online Retailer
Online retailers are the one who have online e-stores and delivers based on orders received through online channels . They offer better convenience and sometimes lower prices.
6. Convenience Store
Dedicated stores in housing societies or residential areas who cater to a set of customers at higher customer service and delivery options at a premium. They stock all the goods required for the particular set of customers.
Examples of Retailers
Examples of some of the big retailers in the world are Walmart, Carrefour, Tesco, Metro AG, Kroger etc.
Hence, this concludes the definition of Retailer along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us