Strategic Workforce Planning- Impact of HR Metrics and Business Analytics
Over the last few decades, a doctrinal shift has been observed across the organizations across the globe. The efforts of an organization have been customer centric rather than product centric. This ideology shift inculcates from the diversified product lines, service ranges and the magnitude of options available with the clients and customers. Quality, precision and cutting edge technology are the undisputed call of the day and almost very organization adheres to these standards. The pertinent question arising is that why a certain organization is a market leader although its competitors are more or less equivalent in terms of quality, pricing, serviceability and availability. The answer lies in the capability of the Human Capital Management.

Image Courtesy: freedigitalphotos.net, cooldesign
The strategic initiatives of a company which are predicated on business environment and internal capability in terms of resources need clinical execution which is systematic and detailed. According Porter (1985) an organization must use resources which are valuable. Management of tangible resources like material, money et al are all dependent on the efficiency and effectiveness of the man-power within an organization. The top-level management have to invest in HRM to ensure that this critical and most fundamental aspect of any organization is productive, creative and providing with a sustainable competitive edge. To do so, the objective should be to ensure that Human Resources evolve into a more strategic role rather than a transactional, administrative functionality. The values, missions and both the long term & short term goals and corresponding action protocols have to be in-line with the human capital management and this needs to be encapsulated across the organization, cutting through geographical, gender, racial and intellectual boundaries through the depth and breadth of the entire business. Strategic Human Resource management provides with a direction pertaining to organizational design, employee value proposition, competency assessment , skill development and succession planning through focussed training and cultivating a culture of progressive employee engagement for man-power enrichment and empowerment.
The basic premise is to establish a structure where the entire business model is intermingled in every facet and at varied levels of hierarchy with human management such that plans, actions and outcomes of the human component directly affect the business outcome both in terms of bottom-line and top-line.
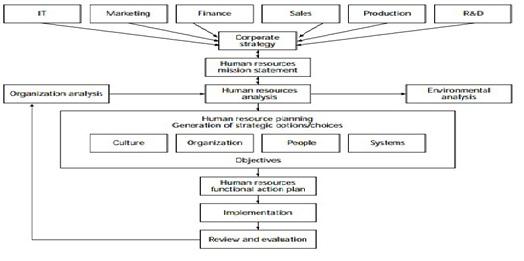
Fig. Organizational HRM Strategy Chain [1]
Human Resource Analytics:
The requirement for Human Resources to be viewed as a strategic collaborative partner affecting outcome of the business, hinges upon the direct impact it can cause to the top-line and bottom line business. To address this issue, the fundamental concepts of capturing return on investment, addressing cost-optimization and incorporation of best practices with respect to core HR verticals has to be supported by structured data, fact or evidence. To cover this entire gamut of expectations, the focus should be shifted from the conventional modulus operandi to HR analytics and Big data. Analytics covers the entire spectrum of data generation, storage, and conversion by analytics of the raw data into useful information. The purpose is to show the advantages of an accurate tracking and analysing mechanism, how it can be implemented, what strategic planning needs to be incorporated behind it and how it will help in providing conclusive facts which can be used by the top-management for making value added decisions.
It is however critical that HR analytics has an Integrated Approach. It implies pulling in multiple HR processes to tackle strategic issues, e.g. in Succession planning using HR analytics, the components of performance evaluation, analysis of input and output from trainings, engagement of the employee in terms of contribution, efficiency, effectiveness etc. should all be factored in a clinical and systematic manner.
It has to further transcend from being mere transactional into a Predictive Analysis tool. This has to be achieved by sound analysis of tracked data by effective analysis clubbed with advanced statistical knowledge.
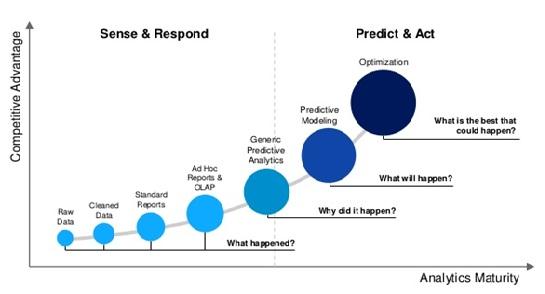
Fig. Evolutionary Phases of HR Analytics [2]
HR Analytics as a component of strategic management:
Aligning core business objectives viz. Revenue, rewards for stakeholders, customer satisfaction et al., with Human Capital management has to be bridged with measurable and factual data. It has to be supported by financial figures and needs to highlight the ROI to find credibility for the various functionalities which are operational. The reason behind this is to establish the direct co-relation of investments in people and how it is yielding tangible profits which is the core necessity. This cannot be merely depicted by qualitative or superficial data, but needs a structured pattern.
The following structure illustrates a rational chain of processes aimed at providing the top-management with a robust monitoring and decision making tool.

Fig. Strategic Components of HR Analytics
The process driven HR analytics process which is capable of incorporating the salient features , such that all parts of the strategic plan get implemented in the process can be best described with a diagrammatic representation of the HR analytics value chain:
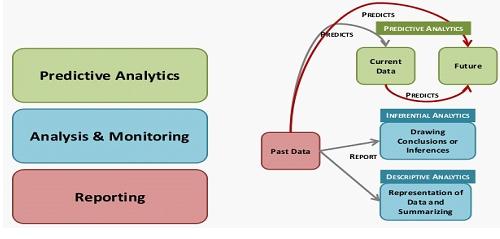
Fig. Critical Components of Analytics and mutual correlation
Analyzing the strategic components of HR and their ROI factors:
4.1: Recruitment & Selection - Recruitment and Selection is a major HR function that encompasses all the practices and decisions that are the part of an organization. The extent of strategic integration in the field of Recruitment and Selection [3] can be understood by certain indicators (viz. effective job analysis and well defined job descriptions, timely supply of qualified workforce, effective selection criteria, et al). An effective conduction of job analysis and targeting the right candidates ensures that there is a good match between applicants and jobs.
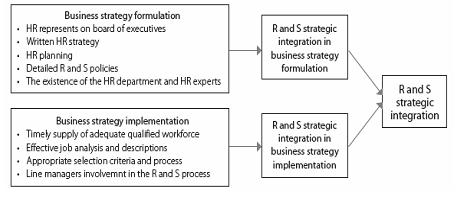
Fig. Strategic Recruitment and Selection Model
The information pertaining to various facets can be generated, stored and measured using modern HR analytics tool and comprehensive mathematical information can be derived out of it to aid the decision making process at the strategic top management level few of the key HR metrics which can be used here are as enumerated:
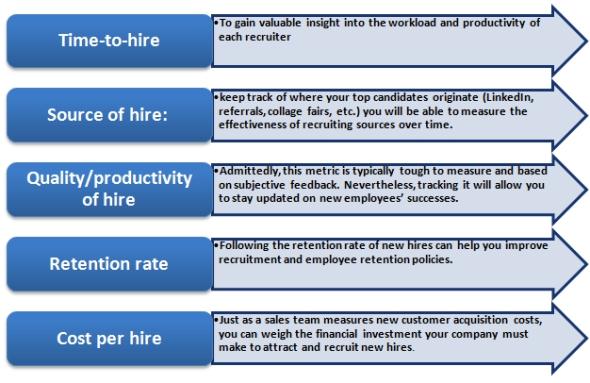
Fig. Key Metrics of Recruitment and Selection
4.2: Training & Development - Training as an organizational intervention is deemed to be a set of well thought out activities that are aimed at facilitating knowledge, attitude and skills among people in the organization, to enhance their current skills and focus on reaching the organizational goals. It is an indispensable tool that accounts for an enterprise's long term objectives and goals like development of new products, expansion in the global market, developing a workforce with core competencies.[4] Rapid changes in the technological scenario, exportation of jobs, shortcomings in the formal education system, global competition, ageing workforce and downsizing are some of the major reasons which stress upon the need of focusing unto the training needs of an organization.
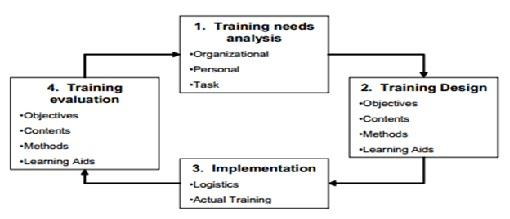
Fig. Strategic Training and Development Model
Some of the key metrics which can be effectively created and monitored to ascertain the strategic importance are as follows:
1. Training hours per employee = Training and development hours / No. Of total Full time equivalent of all full time, part time & contingent labour hours
2. Percentage of employees trained = No. Of employees / Total number of FTEs
4.3: Succession Planning - The core focus of succession planning is provision of in-house replacements and retention of key talent. It prepares the individuals in the organization for potential challenges and accelerates their development by provision of challenging, growth-oriented and rewarding career opportunities. Author William Rothwell's book Effective Succession Planning dictates that Talent Management should be an integral component of Succession Planning and must anticipate change, as opposed to merely acting as 'replacement planning'. Defining Competencies (viz. knowledge, technical skills, leadership qualities, analytical skills, business acumen, etc) is an important part of defining key positions within the organization.
Succession planning in view of a contributor to strategic goal attainment has multiple variables to it and the same can be illustrated with the help of the following diagrammatic representation:
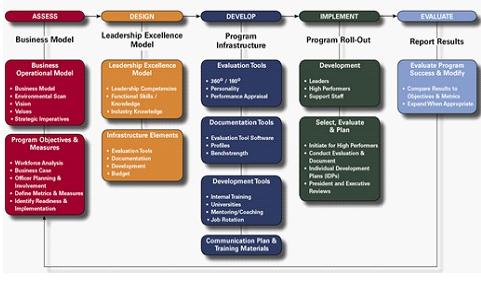
Fig. Strategic Succession Planning Model
4.3: Performance Management system - Performance Management plays a pivotal role in any organization's HR framework. Its benefits extent to enhancement of individual and team performance, as well as fulfilment of organizational goals. A well designed Performance Management System can stimulate the managers to develop strategic plans, set precise targets, track performance and sustain value creation, thereby providing the organization with a competitive advantage. The core focus should be on future performance planning, as opposed to retrospective appraisals. Furthermore, periodic evaluation of the human resources ensures that the employees are motivated and committed and can achieve their full potential for their individual benefit as well as that of the organization.
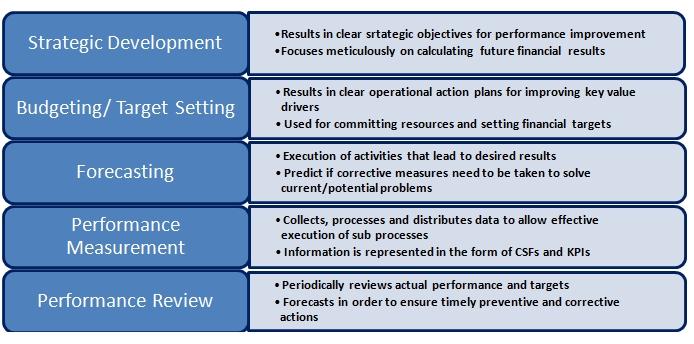
Fig. Key Components of Strategic Performance Management System [5]
Conclusion:
A need for proactive workforce planning is essential. The micro and macro economic conditions, technological changes and business demographics are altering at a rapid rate. The presence of a strategic workforce plan provides a multi-dimensional approach towards building human capital, identifying skills and creating the leaders of tomorrow. A strategic plan also will help mitigate risks, reduce attrition and develop a value added training culture for the organization. To achieve this mammoth task, the premise of establishing HR analytics in yielding accurate and real time information, complemented by strategic action should be the underlying principle in ensuring the attainment of the goal & objectives.
This article has been authored by Sannah Manuja & Orijit Ghosh from XIMB
References:
[1] Larcker, David, Organizational Strategy, Business Models, and Risk Management, 2011. Available at < http://www.gsb.stanford.edu/sites/default/files/documents/06.Business%20Model%20and%20Risk_1.pdf> [Accessed on 22 August 2014]
[2] Dries, Coupe, Predictive Analysis: More than just a buzz. Available at <http://blog.delawareconsulting.be/DelawareBlog/2014/01/predictive-analytics-more-than-just-a-buzz/> [Accessed on 21 August 2014]
[3] David, Jenifer, Recruitment, Development & Retention Strategies. Available at https://www.onecaribbean.org/content/files/RecruitmentstrategiesJeniferDavid.pdf [Assessed on 22 August 2014]
[4] SHRM, Research Quarterly, Strategic Training and Development: A Gateway to Organizational Success, 2008. Available at <http://missionfacilitators.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/Strategic-Training-Development-SHRM-2008.pdf> [Accessed on 21 August 2014]
[5] Eckerson, Wayne, Performance Management Strategies: How to Create and Deploy Effective Metrics, 2009. Available at http://www.microstrategy.com/Strategy/media/downloads/white-papers/TDWI_Performance-Management-Strategies.pdf [Accessed at 21 August 2014]
Views expressed in the article are personal. The articles are for educational & academic purpose only, and have been uploaded by the MBA Skool Team.
If you are interested in writing articles for us, Submit Here
Share this Page on:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
All Business Sections
Write for Us