- Business Concepts ›
- Operations and Supply Chain ›
- Selective Distribution
Selective Distribution
Definition & Example
This article covers meaning & overview of Selective Distribution from operations perspective.
What is meant by Selective Distribution?
Selective Distribution is a type of distribution strategy that lies and operates between intensive and exclusive distribution. Selective Distribution involves using more than one, but lesser than all the intermediaries and distributors who carry the company’s products on a basis of a company specific set of rules. Mostly furniture, television and home appliance brands are distributed in this manner.
There are total 3 major distribution strategy types: Selective Distribution, Intensive Distribution and Exclusive Distribution.
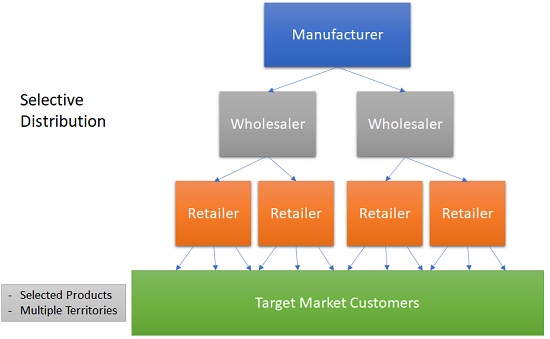
Selective Distribution Example
The best examples would be of Whirlpool and General Electric who sell their major appliances through dealer networks and selected large retailers. They develop a good working relationship with these selected channel partners and expect a better-than-average selling effort.
Read More
Advantages of Selective Distribution
The advantages of selective distribution are
1. good market coverage,
2. increased control and
3. reduced costs as compared to intensive distribution.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team which comprises of MBA students, management professionals, and industry experts. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us