Positioning - Definition, Importance, Types, Factors & Example
What is Positioning?
Positioning is the process of creating a distinct mental position or image of a product or a service in the mind of the customers as compared to other brands in the market. Positioning helps to create a unique image of the brand and the product in the mind of the consumers in comparison with other products or brands which are already existing in the market. In marketing, the positioning concept is followed after the market segmentation where the market is broken down and a target group for their product is identified using targeting strategy, which is collectively known as STP marketing strategy. After selecting a niche market, it helps to create an impression in the customers mind. Companies create a positioning statement for their brand, product or service which helps customers identify with the business.
Every marketer considers the brand positioning as one of the most important aspect of overall brand creation. People have different perception about a brand based on how the brand was positioned in the market.
Importance of Positioning
Positioning is a very important concept in marketing as every company and marketer plan to create unique positioning for new product launches as well as existing products or services. Without a proper positioning statement and process, any product or service would not be able to sell in the market properly. The audience would not be able to get that unique message and position the product wants to convey. If the positioning is same as competitors then the audience might not able to differentiate or chose it among others.
A good positioning covers both points of parity as well as points of differentiation in the market as compared to the competitive landscape. Through clear positioning only, the customers would be able to clearly match the product/service with their needs resulting in potential purchase.
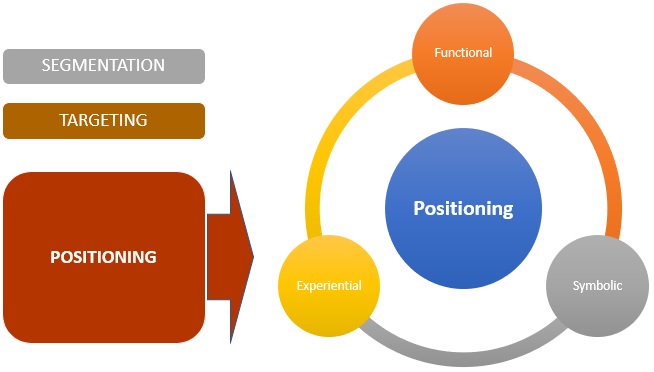
Types of Positioning
Positioning is broadly classified into three types:
1. Functional
This is used when the brand or products provide solutions to problems and provide benefits to customers. It focuses on the function, benefit or utility that it gives to the customer.
2. Symbolic
This is useful for creating a brand image which helps create brand equity, a sense of social belongingness and ego-identification. It is when a customer has an affection, social connection, ego identification etc. with the product.
3. Experiential
This creates sensory and cognitive simulation in the minds of the customer. It is one of the basis of the experiences which a customer can relate to.
Companies use a positioning process, which is step-wise method to place the product or service in the right way in the consumer's mind. If a company decides to change the way people perceive a brand, then they revamp the logo, slogan etc. of that brand. This process is known as repositioning of the brand, which helps create a different image of the brand.
Key Factors of Positioning Strategy
Positioning is critical for any brand, product or service to ensure an impression is created on the mind of the consumer.
The main factors considered by a marketer for creating a strategy for a brand or product are:
1. Product Features
Positioning can be done on how the product looks, feels, appears etc. The main features of the products can be used to highlight the value and create the positioning around it.
2. Utility & Benefits
It takes into account the value which a product gives and which needs are solved. It should show the clear benefit in terms of dollar value or number
E.g. 50% savings in electricity expenses can be a clear benefit to a customer.
3. Use Categories
This defines how the product can be used. All the different use cases and scenarios can be used to create a compelling positioning.
4. Occasion
The time, event or the occasion when the product can be used. Association with an event like New Year can lead to strong positioning in the minds of customer.
5. Competitive Comparison
Positioning can be done when compared to a competitive offering. This is done by a lot of companies to use existing competitive positioning and make it better using points of parity or points of differentiation to create a better positioning.
In positioning the product is differentiated based on 2 things to achieve competitive advantage: -
Points of Parity (POPs)
The positioning is done on the basis of mostly similar elements compared to a competitor.
Points of Difference (PODs)
In this case, there is a clear difference in the product offerings vis-à-vis the competitor.

The above product positioning graph for laptop, i-pod, netbook and kindle shows the benefits in terms of different parameters. This method of understanding positioning is also known as perceptual mapping or brand mapping.
Examples of Positioning
Positioning examples of products can be understood on the basis of various parameters, characteristics and features of products & services. Some key examples are:
1. Aspirational: Nike (Just Do It).
2. Emotional: Coca Cola (Open Happiness).
3. Price-Based: Rolls Royce (Trusted to Deliver Excellence).
4. Problem Solution: Head & Shoulders shampoo (Dandruff free hair).
5. Benefits: Colgate (Prevents cavity and fresh breath).
Hence, this concludes the definition of Positioning along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us