- Articles ›
- Entrepreneurship ›
- The Entrepreneurship Ecosystem - Individuals, Organization and Institutions Articles
The Entrepreneurship Ecosystem - Individuals, Organization and Institutions
The entrepreneurship ecosystem refers to elements which include individuals, organizations or the institutions. They are outside of an individual entrepreneur & are conducive to the choice of an individual to become an entrepreneur & the probabilities of the success of that person after the launch of his project. The organizations & the individuals which represent these elements are referred as the entrepreneurship stakeholders. Stakeholders, being more entrepreneurship in the region, are any of the entities which actually or potentially have an interest in there. Entrepreneurship stakeholders include schools, government, private sector, universities, investors, family businesses, entrepreneurs, banks, research centers, social leaders, labor representatives, military, lawyers, students, communes, cooperatives, private foundations, international aid agencies as well as the multinationals etc.
In order to create a sustainable entrepreneurship, an isolated element in this ecosystem is never sufficient. In the areas where we have extensive amounts of entrepreneurship including regions of Boston, Silicon Valley, Israel & New York City, most of those ecosystem elements are strong & have typically evolved in the tandem. Similarly, formation of these ecosystems advises that the governments or the societal leaders, who are willing to foster more entrepreneurship as a part of the economic policy, should strengthen such elements simultaneously. But recent research indicates that the government policy is mostly limited to develop the entrepreneurial ecosystems.

image:pixabay
In 2010 July, the HBR published an article written by Mr. Daniel Isenberg who was a Professor of Entrepreneurship Practice at the Babson College. The name of the article was - How to Start an Entrepreneurial Revolution. In this, he describes about the environment in which entrepreneurship inclines to thrive. Referring to the examples from across the world, the article suggests that the entrepreneurs are successful when they have sufficient access to the human power & also the financial as well as the professional resources they need. Also, they should operate in the environment where the government policies do not discourage the entrepreneurs but ultimately encourage & safeguard them. This network can be termed as an entrepreneurship ecosystem.
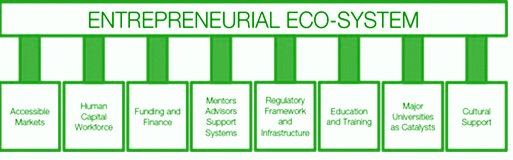
It could be a group of the companies, also including the start-ups & 1 or more coordination entities, since they share the similar goals; they decide to create a network or an organization, to explore an economy of the scale combined with the flexibility as well as the strong entrepreneurial drive. Economies of scale is explored in the business functions like the financing, business development, marketing communications, market analysis, human capital management, IT or MIS infrastructure, financial & accounting management while every participating start up focuses on the research & development, legal support, product Management combined with sales, pre sales & the after sales support.
There are some necessary conditions to define the healthy ecosystem. Some of which are mentioned below:
• The ecosystem must be tailored around its unique environment. It should not seek to be something which it is not like the next Silicon Valley or anything like that.
• The ecosystem should operate in an environment with the reduced bureaucratic obstacles where the government policies should support unique needs of the entrepreneurs while tolerating their failed ventures.
• It must actively encourage & invite the financers to participate in the new ventures. But always remember that access to the money is not barriers free for those who are planning a new business venture.
• The ecosystem should be reinforced by the government, an academic or the commercial organizations.
• The ecosystem should be relatively free from or must be able to change the cultural biases against the failures or operating of a business.
• It should promote the successes & advertise itself. It in turn helps in attracting the new projects.
• The ecosystem must be supported by the dialogues among different entrepreneurship stakeholders.
Increasing the no. of high growth firms is a major focus for the industry policies now in the developed countries. The existing approaches are proving to be ineffective. Just creating a supportive framework condition is not sufficient. Creating the favorable environments for the business start-ups is not leading to the formation of the more HGFs. Also, the transactional forms of the support for the HGFs like financial assistance are proving to have the limited effectiveness post the start-up is done. The entrepreneurship ecosystem approach has emerged as a response. It recognizes that HGFs flourish in the distinctive types of a supportive environment. Distinguishing features of an entrepreneurial ecosystem includes a core of some of the large established businesses, including those which have been entrepreneur led & proved to be the entrepreneurial blockbusters; entrepreneurial recycling whereby the successful cashed out entrepreneurs reinvest their time, the money they have earned as well as the expertise in supporting a new entrepreneurial activity; & an information rich environment, where this information is both accessible as well as shared. The deal maker is a key player in this context.
He is involved in a fiduciary capacity in some of the entrepreneurial projects. The other important aspects of an entrepreneurial ecosystem include the availability of the start-up & the growth capital, its culture, universities & the service providers & also the presence of the large firms. But the studies have taken a static approach for the study of entrepreneurial ecosystems. It largely ignores their origins & the stimulus as well as the processes of becoming the self-sustaining for them. Creating the entrepreneurial ecosystems poses many different challenges for the policy makers. There are some general principles which need to be followed. Policy intervention needs to take a holistic approach.
It should focus on the following:
• the entrepreneurial actors within the ecosystem
• the resource providers within the ecosystem
• entrepreneurial connectors within the ecosystem
• & an entrepreneurial environment of the ecosystem
Finally, it is important for the policy makers that they should develop the metrics in order to determine the strengths & the weaknesses of an individual ecosystem so that their strengths & the weaknesses can be assessed to identify whether & how to intervene, & monitor the effectiveness of such interventions over a specific period of time. Formidable challenges are posed by all, such as what to measure, approaches to the measurement as well as an access to the data at the appropriate geographical scales.
This article has been authored by Gopal Zavar from SIMSR
References:
-http://www.technologyreview.com/article/14761/
-https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Entrepreneurship_ecosystem
-http://www.technologyreview.com/article/14761/
-http://www.nytimes.com/2008/12/26/business/worldbusiness/26peso.html?pagewanted=all&_r=1&
Views expressed in the article are personal. The articles are for educational & academic purpose only, and have been uploaded by the MBA Skool Team.
If you are interested in writing articles for us, Submit Here
Share this Page on:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
All Business Sections
Write for Us