- Business Concepts ›
- Marketing and Strategy ›
- Market Mechanics
Market Mechanics
Definition & Meaning
This article covers meaning & overview of Market Mechanics from marketing perspective.
What is meant by Market Mechanics?
The laws that govern the working of the market system are called as a market mechanism. Market mechanics are governed by certain fundamental laws of the market called Law of Demand and Supply.
The force of demand and supply determines the price and quantity of goods and services which are offered for sale in a market. If demand is higher than supply then price of the product is high. Also, if demand is lower than the supply then the product is sold at a lower rate.
The key points here are that satisfaction of the society should be maximized at minimum cost; also all resources should be fully utilized to achieve this.
For example: Imagine that two producers of detergents are in competition (Tide by P&G and Active wheel by HUL). If consumers swing away from Tide to Active Wheel, demand falls for the Tide and rises for Active Wheel. In response to falling demand, P&G will lower the prices, whereas HUL will increase the prices in response to rising demand. The consumers react to this increase in price by shifting from Active Wheel to Tide. To tackle this HUL will also lower the price and thus at some point the demand for both the products will return to the original level and also their prices will be similar to achieve equilibrium.
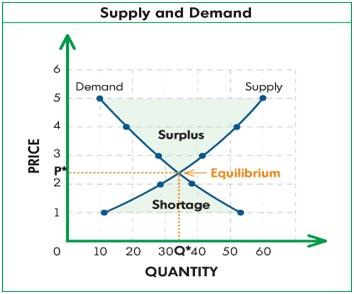
Hence, this concludes the definition of Market Mechanics along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team which comprises of MBA students, management professionals, and industry experts. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us