- Business Concepts ›
- Marketing and Strategy ›
- Customer
Customer
Definition, Importance, Types & Example
This article covers meaning & overview of Customer from marketing perspective.
What is meant by Customer?
Customer is an individual, group of individuals or an organization who receive or may receive goods, services, products or ideas from another individual or a company in return of value which can be money or anything of equivalent value. Customer forms the backbone of business. Usually more is the number of customers, more is the business thriving and vice versa. Business needs customers to buy their products or services. A customer may not be buying your product right away but may buy it in future but still remains part of your target customer group.
8 Types of Customers with Examples
Customers can be of various types depending upon their ability to buy products or services.
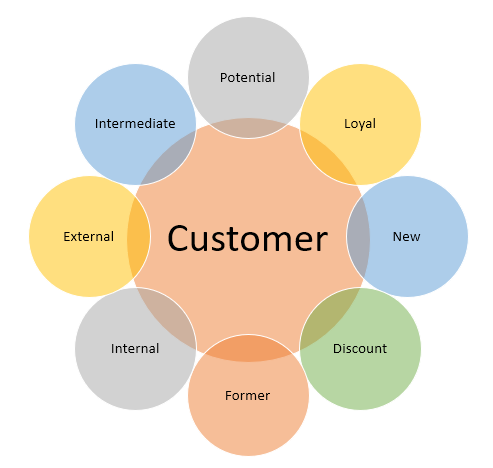
Below are the 8 different types of customers:
1. Potential Customer
Kind of person who is very likely to buy the product or service offered by the business. e.g. a customer looking for an apartment in a particular area becomes a potential customer for the local realtors who would have a flat which will suit the requirements of the customer.
The customer might end up buying the apartment. Potential customers can present an opportunity for the business to sellers and after qualification can convert into a quote stage and eventually result in an order or a sale.
2. Loyal Customers
Those who are loyal to one business and repeat the purchases irrespective of minor changes in parameters like price, quantity etc.
e.g. a customer who buys the same airline's ticket irrespective of price.
3. New Customer
The customers who have used the product or service for the first time from a particular organization. Such customers can be switching from a competitor brand or may be new entrant into the market.
e.g. a person buying car for the first time after a salary raise. From the perspective of the organization, a new organization would acquire new customers from the market either by launching a new product category altogether or launching a competitive product offering in the market.
4. Discount Customer
Those who only buy or use the offering because it was on discount or offered a cashback. These people are more likely to switch brands easily if prices reduce unlike loyal customers. e.g. A customer who takes a different flight based in the discounts offered though the preferred airline brand was different based on past travels.
5. Former Customers
Those who were once buyer of one business and became buyers of a new business because of some reason. These people would still be potential customers as they have already tried the product or service once.
e.g. A person who used to buy a specific beverage switched to a more healthier option offered by a competitor.
6. Internal Customer
One who is connected to your organization and is internal to your organization. These for example are your shareholders, employees & other stakeholders.
7. External Customer
An external buyer is a buyer of your services and products but external to your organization. An example of your external consumer could be people buying your products in the marketplace.
8. Intermediate Customer
Those who purchases the goods for re-sale e.g. retailers. The customers are part of a longer supply or value chain.
Read More
Importance of Customer
A customer is the foundation for any business. A business cannot exist without a buyer base. A buyer will pay for the offerings made by business and keep it going. It is very important for a business to manage the customer really well as the same person can become loyal and repeat translating into more business. These happy buyers would advocate and refer your business to other potential buyer bringing in more business. In short, a business cannot operate without business hence customer is of paramount importance to any business.
All businesses aim to meet the customer needs and demands. They make sure that the customer gets value from the money paid. The following parameters show how important the customer is:
1. Customer Experience
These days the customer experience is one of the most important parameters in the world. The customer experience doesn't start after buying a product but it starts from the moment customer notices a product. The customer can take decision based on positioning, packaging, colors, branding, sales approach, store experience or any other parameter. All form part of the customer experience.
2. Customer Satisfaction
Customer experience need to convert into customer satisfaction. A customer needs to be sure and satisfied before and after buying a product. If any of the parameters are not in favor then the customer dissatisfaction may happen and current or subsequent sales might not happen.
3. Customer Support
Customer might need service and support at any point in the sales and after-sales cycle. Customer service has become of the pillars of successful businesses highlighting how important the end customer is.
Business Categories of Customer
Apart from the types of customer we saw above, there are some other categories of customers based on the businesses.
1. B2C (Business to Consumer)
This one of the most important categories. All the consumer companies which sell to individual customers are in the B2C segment. FMCG/CPG companies selling soap, toothbrush, shampoo or even apps these days can be termed as B2C examples.
2. B2B (Business to Business)
This is when the businesses send directly to businesses or enterprises. These are large scale sales and require longer interaction with the group of customers and representatives to close the deal. An example can be group insurance or laptops for all the employees of entire organization
These days even C2C and C2B are developing into complete business paradigms
3. C2C (Customer to Customer)
These are upcoming peer selling models. Many popular online platforms have enabled this where individual customers sell to other customers. Most of the products here would again be used or refurbished products. An example can be one customer selling used smartphone to other customer on a marketplace
4. C2B (Consumer to Business)
There are the business models where the customer sells something to business. Second hand car markets can come under this category.
Customer vs Consumer
A consumer is the person who actually consumes the products or services, whereas the customer is simply the purchaser & need not be the consumer. The intermediate buyers are never consumers as they buy for re-sale. The purchaser of industrial goods & services is called industrial customers or business to business customers.
Customer Service and Support
Customer Service is an important aspect of modern day business. Once a person buys a product or uses a service, the scope of customer service starts immediately. A buyer may face some defect or may need further information to use the offering.
For example, a new SIM card user after installation of card may not be able to place calls so there has t be a way to connect to SIM card provider for help. If the customer service support solves the issue, the buyer is happy and values the business but if there is no way to contact the business it can lead to loss of consumer and issues in future.
Hence, this concludes the definition of Customer along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team which comprises of MBA students, management professionals, and industry experts. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us