- Business Concepts ›
- Marketing and Strategy ›
- Decision Making Process
Decision Making Process
Definition & Stages
This article covers meaning & overview of Decision Making Process from marketing perspective.
What is meant by Decision Making Process?
Decision Making Process refers to the different stages of decision making that a consumer undergoes before, after and during the purchase of product or service. Decision making process is important for a marketer to understand what goes inside the head of consumer and how to make him/her purchase your product or service.
The decision making process of a customer includes different levels of purchase decisions, i.e. extensive problem solving, limited problem solving and routinized choice behaviour. This is an important concept in marketing which companies need to understand so that they can target customers effectively and increase sales.
Decision Making Process Stages
Decision making process consists of five stages. However, it is not necessary that all the buying decisions go though each and every stage.
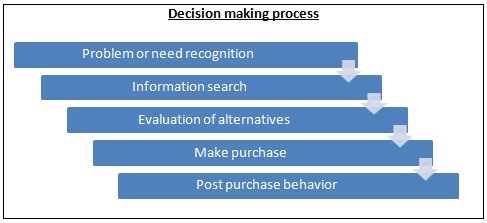
I. Problem or need recognition: The first stage in the decision making process or the buying process starts with need recognition. The consumers identifies gap between his current state and desired state. A need can be triggered by internal or external stimuli. Internal stimuli includes personal needs experienced by the consumer, such as hunger, thirst etc. Advertisements, word of mouth are external influencers which can also trigger needs.
II. Information search: In second stage of decision making process, customer tries to gather as much information as possible. But it depends on how strong the need is. If the need is too strong, customer might skip this stage and go for purchase. If not, information search process begins. Information search can be categorized into internal and external research. Internal search refers to recalling past experiences with the product. External search is conducted when customer tries to seek information from personal sources (family, friends etc), Commercial sources (advertisements, sales people) or public sources (newspapers, television etc).
III. Evaluation of alternatives: In the third stage of decision making process, customer evaluates all the alternatives available in the market. It either occurs separately or in conjunction with information search. The important determinant in this stage is the degree of involvement customer may have with potential product. When a purchase is highly involving, customer might go for extensive evaluation. Examples of highly involving purchases are buying a car, house etc. It is important for marketer to stress on important features of the product in such cases. Consumer moves to next stage once value of all alternatives have been assessed.
IV. Purchase: Actual buying of product occurs in the fourth stage of decision making process.
V. Post purchase behaviour: In the last stage of decision making process, consumer analyses whether product was useful to him or not, whether the product fulfilled his need or not. If the satisfaction level is high, consumer will become loyal customer of the brand. Marketer’s goal is to make sure that buyer feels positive about their purchases.
Hence, this concludes the definition of Decision Making Process along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team which comprises of MBA students, management professionals, and industry experts. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us