- Business Concepts ›
- Operations and Supply Chain ›
- Assemble To Order (ATO)
Assemble To Order (ATO)
Definition & Meaning
This article covers meaning & overview of Assemble To Order (ATO) from operations perspective.
What is meant by Assemble To Order (ATO)?
You must have seen number of unsold automobiles in a showroom and wondered if it is costing anything to the showroom owner. The answer is Yes. Showroom owner has to keep the stock until it is sold and this adds towards his factor cost. Also, if a customer demands for some customization, that can’t be met as it is a finished product. So the immediate solution that comes to the mind is that the owner should keep only the inventory which is necessary to produce and assemble it once he receives the order. This is exactly what we are going to discuss in this article, concept of Assemble to Order (ATO).
It is a production model where the final goods are produced once the manufacturer receives the order from the customers. The components are already produced and stored at the site. This method is different from the build to order method where the manufacturer starts producing from the scratch after customer places his order. It is advantageous for the customer as he gets the customized product in short time and also the cost for keeping the inventory reduces for the manufacturer.
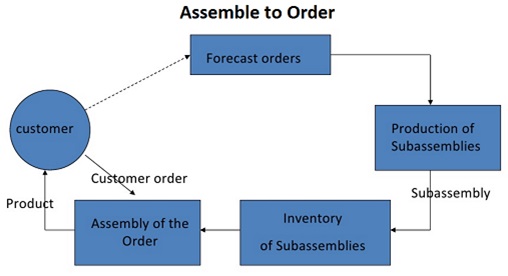
Figure: Steps followed in Assemble to Order methodology
Where to use ATO?
ATO technique is beneficial for business where huge number of customers is demanding for customized products. Since the make to stock, i.e. manufacturing and keeping the stock before the customer places the order is not feasible over here due to varied customer preferences, the production manager uses assemble to order technique and produce only the common sub parts before
Example: One well known example for ATO technique is the success of Dell Computer’s. Company allows the customers to choose among several processors, monitors, disk drives etc. There can be numerous combinations of the components which a customer can choose. The producer keeps the stock of parts and assembles it once he receives the order from the customer and delivers the customized product in almost no time.
Advantages of ATO:
• Sub parts can be replaced in future once they become obsolete
• Higher inventory turnover ratio, leading to low cost
• Capability of producing customized product
• Quick delivery
Hence, this concludes the definition of Assemble To Order (ATO) along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team which comprises of MBA students, management professionals, and industry experts. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us