- Business Concepts ›
- Operations and Supply Chain ›
- Operations Management
Operations Management
Definition, Importance, Parameters & Example
This article covers meaning & overview of Operations Management from operations perspective.
What is meant by Operations Management?
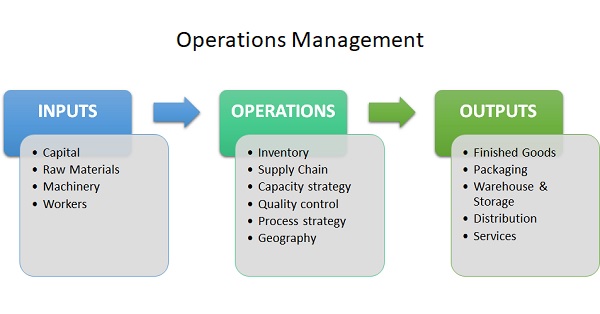
Operations management is a field of business which deals with how a product is planned, created & distributed. Operations management focuses on activities like managing inventory, capacity planning, production & process, supply chain management, packaging, distribution, warehousing etc. All factories, manufacturing plants, construction, agriculture & even service sectors follow the basic principles of operations management.
Importance of Operations Management
Every organization understands the market, customer need, demand & supply analysis and manufactures goods & services based on that. Operations management focuses on evaluating, monitoring operational processes of manufacturing, maximizing productivity, reducing poor processes, increasing efficiency, quality maintenance & ensuring finished goods are distributed across geographies.
Read More
Operations Management Parameters
Some of the key elements of operations management for any business are as follows:
1. Demand Supply Analysis- Understanding product demand, supply requirement, business forecasting etc are critical in manufacturing operations.
2. Inventory management- The management of raw materials, quality of goods, finished products etc is critical for business.
3. Supply chain management- Operations management includes supply chain management ie product storage, distribution etc.
4. Capacity management- Production capacity needs to be evaluated based on demand, productivity, input inventory etc.
5. Process & Layout strategy- Factory layouts, operational processes, production methods etc are critical for business output.
6. Geography strategy- This is an important parameter under operations management to evaluate locations for factories, warehouses, distribution centers etc.
Objectives of Operations Management
Some of basic business activities which are completed include:
1. Generating a desired output basic on demand & supply.
2. Profitability is a key objective by increasing productivity & reducing costs.
3. Ensuring quality of each & every product produced is of the highest standard.
4. The products produced are to be generated in a systematic & sequential manner.
5. Packaging, storage, warehousing, distribution are also key objectives of operations management.
Examples of Operations Management
Some different types of examples are:
1. Consider a shirt manufacturing company. The business of this company is driven by operations management. Raw material cloth input is procured based on output need. Shirt designs, capacity, color, styles etc are planned & output volume is evaluated. Shirts are then produced in a large volume, checked for quality & packaged. After that the shirts are dispatched to different locations & stored in warehouses for further distribution to retailers.
2. Another example is that of an ecommerce company. Ecommerce operations management includes displaying available stock, inventory management etc. Once an order is placed, it is packaged from the warehouse closet to the customer. After that, the goods are picked up & dispatched to the customer. Once the customer receives the product, the same is tracked at every stage & the final feedback is recorded for process improvements.
Hence, this concludes the definition of Operations Management along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team which comprises of MBA students, management professionals, and industry experts. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us