- Business Concepts ›
- Operations and Supply Chain ›
- Warehouse
Warehouse
Definition, Importance & Types
This article covers meaning & overview of Warehouse from operations perspective.
What is meant by Warehouse?
Warehouse is defined as the storage structure build for the defense of the quality and quantity of the stocked up produce. The requirement for a warehouse is felt when there is a time gap between the production of the product and the consumption of products. Warehouses enable the businessmen to carry on production all through the year and sell their products, at any time there is sufficient demand.
Importance of Warehouses
Warehouses are primarily used for storing goods. Need for warehouses occur also because some goods are fashioned only in a specific season but are asked for throughout the year. Likewise, certain products are shaped all through the year but asked for only during a specific season. Warehousing or storage refers to the process of holding and conservation of goods till they are dispatched to the customers.
There is a requirement for warehousing or storing the goods so as to make them accessible to buyers as and when required. Storage allows a company to carry out production in expectation of demand in prospect. By bridging this gap, storage produces time utility.
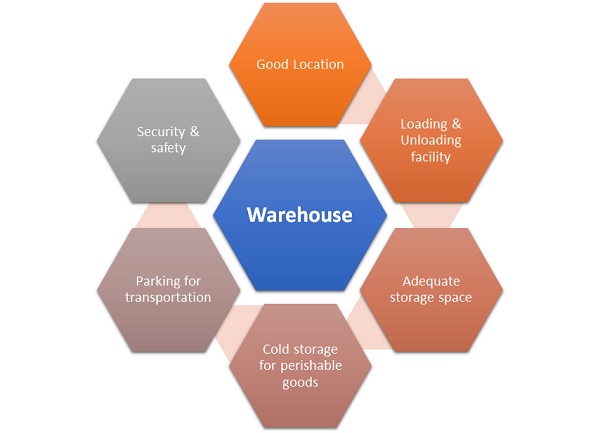
Warehouse Characteristics
Some key factors for an ideal warehouse are:
1. Good Location- near airports, railway stations, highways, and has enough parking space.
2. Loading & Unloading facility for continuous flow of goods.
3. Adequate storage space for accommodating goods of different size & consumption.
4. Cold storage for perishable goods.
5. Parking for transportation media like trucks, lorries, railway wagons etc. to carry goods.
6. Security & safety from fire, theft etc.
Types of Warehouses
There are 5 main types of warehouses:
1. Private Warehouses
These are owned and controlled by big producers and merchants to complete their own storage wants.
2. Public Warehouses
These are a specialized business organization that provides storage amenities to the common public for a definite charge. It may be owned and operated either by an individual or a cooperative society.
3. Bonded Warehouses
These are approved by the Government to accept imported merchandise for storage awaiting the payment of customs duty. They are usually situated near the ports. They are either controlled by the Government or they work under the customs department.
4. Cold Storage & Climate Control
These warehouses use special temperature-controlled mechanisms to ensure that goods like crops, pulses, medicines, flowers & other perishable items are stored for a longer duration.
5. Export & Import warehouses
These storage units are usually at locations where lot of goods flow between countries. These are mostly present at international airports, shipping docks, near highways close to international borders etc.
Hence, this concludes the definition of Warehouse along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team which comprises of MBA students, management professionals, and industry experts. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us