- Business Concepts ›
- Marketing and Strategy ›
- Small and Medium Enterprises (SME)
Small and Medium Enterprises (SME)
Definition, Importance, Factors & Example
This article covers meaning & overview of Small and Medium Enterprises (SME) from marketing perspective.
What is meant by Small and Medium Enterprises (SME)?
SME stands for Small and Medium Scale Enterprises. Small and medium enterprises or SME are small companies with limited manpower & financial turnover. SMEs are those companies whose personal numbers falls below the set criteria. SMEs or small and medium enterprises are defined differently in every country, some countries define it on the basis of employees in the enterprise whereas other countries define it on the basis of investment on the plant and machinery on the enterprise.
In case small and medium enterprise is engaged in manufacturing of goods then a small enterprise in India would have an investment on plant and machinery of more than twenty five lakh rupees but less than five crore rupees. A medium enterprise would have an investment of more than five crore rupees but less than ten crore rupees. In case the SME is engaged in providing services then a small enterprise would have an investment of more than ten lakh rupees and less than two crore rupees and a medium enterprise would have an investment of more than two crore rupees but less than five crore rupees. Priority lending facility is extended to enterprises that come under small and medium enterprises category by the Indian government. Generally this term is used by European countries and some international organizations such as WTO, World Bank and by United Nations. SME’s are the backbone of industrial development. They play an important role in the economy of both developed and developing countries.
Importance of Small and Medium Enterprises (SME)
Small and medium enterprises are very important employers of people and employ a huge chunk of a country’s workforce. A huge amount of the country’s GDP is also generated by SME’s. The government has taken cognizance about these facts and has provided help to SME’s so that they can sustain themselves in difficult market conditions. The government provides priority lending to small and medium enterprises, collateral free borrowing, credit cover facility of upto 85 per cent of the amount borrowed, skill development training program being a few out of the many benefits and facilities extended towards SME’s to sustain.
In some countries upto 97 per cent of the population are engaged employed because of SME’s. Therefore it is a very important way to employ people and the governments of every country should pay attention as well as provide as much support to SME’s as possible.
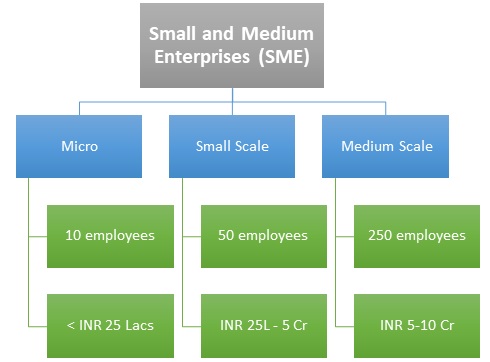
Criteria for Small and Medium Enterprises (SME)
1. Micro Companies: Up to 10 employees/ workers
2. Small Scale Companies: Up to 50 employees/ workers
3. Medium Scale Companies: Up to 250 employees/ workers
Small and medium enterprises can be defined as per manufacturing & service industries as below:
a. In manufacturing Industry:
• Micro Companies: Have investment up to Rs. 25 Lakhs
• Small Scale Companies: Have investment more than Rs. 25 Lakhs but less than Rs. 5 Crore
• Medium Scale Companies: Have investment more than Rs. 5 Crore but less than Rs. 10 Crore
b. In Service Industry:
• Micro Companies: Have investment up to Rs. 10 Lakhs
• Small Scale Companies: Have investment more than Rs. 10 Lakhs but less than Rs. 2 Crore
• Medium Scale Companies: Have investment more than Rs. 2 Crore but less than Rs. 5 Crore
Opportunities in Small and Medium Enterprises (SME)
The various opportunities of growth in SME sector are:
1. Less capital investment
2. Extensive growth and support by government
3. Project Profiles
4. Ease in Raw Material Procurement
5. Ease in Machinery Procurement
6. Growth in demand in the domestic sector due to overall economic growth
7. Have wide potential growth for export as there is much demand of Indian product
Factors Affecting Small and Medium Enterprises (SME)
1. Lack of availability of adequate and timely credit
2. High Cost of Credit
3. Limited Access to equity capital
4. Designing, packaging and displaying of product
5. Inventory Problem
6. Lack of Infrastructures like road, transport, power etc.
Difference Between SME & Large Enterprises
Large Enterprises are enterprises which have an investment of more than ten crore rupees, these enterprises are important for the country and employ a substantial number of people, these enterprises require no support from the government and are self sustaining, governments do tend to attract investment from large enterprises to build a factory in the state so that they can employ workers from the state to work in the factories, investment to build factories would lead to development of townships around that area and also help to increase the GDP of the state as well as the country. Governments provide the large enterprises tax holidays in order to attract investment from them to build factories and offices, they expect the enterprises to employ local people at these places.
Example of Small and Medium Enterprises (SME)
Small and medium enterprises contribute to the GDP of a country in many ways and there are small and medium enterprises in almost every sector one can think of from food processing to manufacturing biomass gasifiers and also business process outsourcing. Some examples in India under these SME’s are DFM foods, which is the manufacturer of CRAX and Natkhat namkeen which are popular snacks in India.
Hence, this concludes the definition of Small and Medium Enterprises (SME) along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team which comprises of MBA students, management professionals, and industry experts. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us