- Business Concepts ›
- Human Resources (HR) ›
- Equity Theory
Equity Theory
Definition & Meaning
This article covers meaning & overview of Equity Theory from HRM perspective.
What is meant by Equity Theory?
The equity theory was proposed by a Behavioral Psychologist, John Stacey Adams. It states that:
‘The motivation of an individual is positively correlated to his perception of justice and fair treatment practiced by the management. The employee seeks a balance between the amount of efforts he pours in (Input) and the kind of compensation he receives (Output). The Individual compares this input-output balance with the other employees in the organization (known as ‘referents’)
Inputs: time, effort, loyalty, commitment, reliability, integrity, tolerance etc
Outcomes: pay, bonus, perks, benefits, praise, reputation, responsibility etc
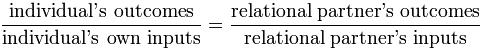
- If the individual’s output to input ratio is lower than the partner’s ratio, he feels under-rewarded and demotivated. The phenomenon is called Equity Tension.
- When the Output-Input ratio is equal to the referents’ ratio, Perfect Equity is said to be developed and the employee feels motivated.
- If the employee’s ratio is greater than the referents’ ratio, the employee feels over-rewarded and again, Equity Tension is said to be developed.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team which comprises of MBA students, management professionals, and industry experts. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us