- Business Concepts ›
- Marketing and Strategy ›
- Hierarchy of Needs Maslow
Hierarchy of Needs Maslow
Definition, Importance & Example
This article covers meaning & overview of Hierarchy of Needs Maslow from marketing perspective.
What is meant by Hierarchy of Needs Maslow?
Hierarchy of Needs by Maslow is the theory of psychology which categorizes the need of human into five types. It was developed by Abraham Maslow in 1943. Maslow proposed that all human beings have a certain number of needs, some being more basic than others. These needs are arranged in 5 levels in a hierarchy in a pyramid with basic or primitive needs at the bottom and complex needs like self-esteem and self-actualization towards the upper level of the pyramid.
5 Levels of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
The five levels of Hierarchy of needs are- from top to bottom-
1. Physiological needs- food, air, sleep
2. Security needs- financial security, shelter
3. Social needs- friends, relatives, family
4. Esteem needs- Dignity, achievements, independence, status, prestige
5. Self Actualization needs- seeking personal growth, self- fulfillment
The important point to note is that all human beings start fulfilling their bottom level needs first before moving towards upper-level needs. For a person, self-esteem and social status are irrelevant when he barely able to satisfy his hunger.
The levels of hierarchy of needs are elaborated as follows:
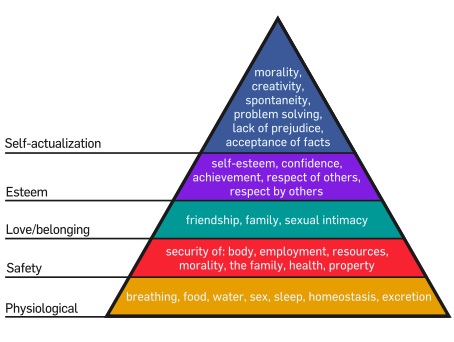
Physiological Need: It is considered as the most basic need of the human and is placed at the bottom of Maslow need Hierarchy pyramid.It should be meet first before meeting the other needs. It means the need associated to human for their existence and survival. Food, shelter and clothing can be considered the example of physiological need.
Safety Need: These are placed above Physiological need in the pyramid and are required only when those are met.
These means the need of protection from the threats. These can be of any form i.e. health, financial, physical etc.
Psychological need: These are the need for love and affection and are required when safety needs are met. In this part a person looks for belongingness with his friends and family.
Esteem Needs: in this human looks for the respect and the sense of acceptance in the society. Fame and glory fulfills the esteem needs of the person.
Self- Actualization need: it is the top most need of the human being and in this person want to achieve success and want to utilize his potential to his best. That means a person want to achieve the highest level he can.
Importance of Hierarchy of Needs
Hierarchy of needs is helpful in determining the key drivers of human behavior and decision-making. In business concept, it enables to understand why certain customers chose one brand over another and why they build strong relationships with particular brands. Brands that focus on satisfying higher level needs in the hierarchy of needs pyramid enjoy better customer loyalty than the brands that focus and satisfy the lower level needs of the pyramid. The brands which are able to satisfy upper-level needs of the customers eventually become irreplaceable for the customers. The reason for this being that higher level needs influence the customer much more than lower level needs ever can.
Advantages of Hierarchy of Needs
Some advantages of Hierarchy of Needs by Maslow are:
1. Easy to understand: Hierarchy of needs as a model is easy to understand and can be easily related to each one of our’s lives as each one of us goes through these stages at some or the other parts in life.
2. It is very relevant in modern-day business as it enables the marketers to segment their customers based on their motivation and level of need to be satisfied and focused on which in turn is useful in product designing, product pricing, planning, and sales channel's design.
3. It enables managers to understand and motivate the employees.
Disadvantages of Hierarchy of Needs
Certain drawbacks of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs model are:
1. The model cannot be verified empirically as there is no method of identifying how much the need should be satisfied at a particular level before the need at other level becomes operative.
2. There can be a particular product or service that not only satisfies or fulfills one level of need but multiple need levels at once.
3. The model fails to keep under consideration the probability of individual differences and cultural differences and assumes that the same order of need levels is applicable to every person and every culture.
Example of Hierarchy of Needs by Maslow
For a person, of all, his physiological needs to be met first to sustain his life like food, water, and oxygen. These are some of the things that the person won't be able to live without. After these needs are met, he will be looking for security, it may be financial security, physical security like shelter. For example, if an employee observes that the company he is working in is downgrading, he will start looking for other alternatives to satisfy his financial need and that will affect his decision making. After this, the person tries fulfilling his social needs. Everyone has a group of people with whom he tries to associate with. Example of this is, associating with co-workers in the workplace.
Now, esteem needs are the needs that the person needs to feel good about him. It can be his hard-earned car, his house or the company he wants to works for, the title he wants to earn. When all three lower levels have been met, the behavior of the person tends towards fulfilling his esteem needs. The topmost level is of self-actualization needs when a person after fulfilling all his bottom level needs move towards fulfilling his self-actualization needs. Under these needs, a person focuses on becoming a better version of himself and make efforts to reach his highest potential.
Hence, this concludes the definition of Hierarchy of Needs Maslow along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team which comprises of MBA students, management professionals, and industry experts. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us