- Business Concepts ›
- Marketing and Strategy ›
- Target Revenue
Target Revenue
Definition, Importance & Example
This article covers meaning & overview of Target Revenue from marketing perspective.
What is meant by Target Revenue?
Target revenue is the revenue or earning which a company is targeting for a given period. Target revenue is the aspirational revenue figure which the company wants to achieve. Target revenue can be set for a year, quarter, month or any particular activity.
Revenue is the measure of the total amount of sales made by a company during a specific time period. It comprises the top line of a company’s financial statements. A company can have 3 types of revenue- the target revenue, the forecasted revenue and the actual revenue. The forecasted revenue is what is forecasted based on past data and the actual sales revenue is what the company meets in true sense.
Importance of Target Revenue
Marketers understand that all objects of operations and functions revolve around the target revenue. The marketing department conveys the target to the operations and finance departments. Strategy and schemes are implemented to meet the target sales. Marketers are keen to set up high and realistic target revenues.
This could be done by increasing quantity sales or increasing the price of the product. Once the target sales is fixed, things move backward which is known as backward scheduling. All functions work in close coordination to achieve the target revenue figures.
Read More
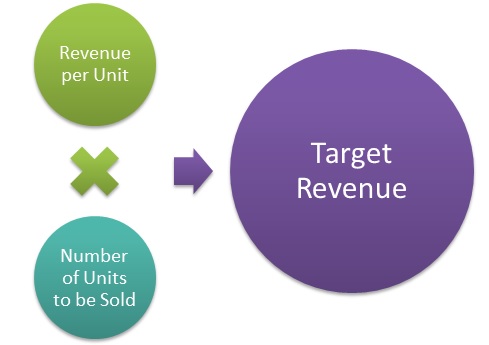
Target Revenue Formula
The formula for target revenue can be written as:
Target Revenue = (Revenue per unit sold x Total number of units to be sold)
This is calculated for a given time period.
Difference Between Target Revenue, Forecasted Revenue & Sales Revenue
Target revenue is the ambition which a company sets to achieve in a given period of time. Based on past data, it also evaluates forecasted revenue and at the end of the time period, it has the actual revenue.
Forecasted Revenue: Companies have past years’ data on sales and net income. Regression and percentage of sales are some of the methods that can be applied for forecasting base on trends. The revenue thus obtained, through regressing past years’ data is the forecasted revenue. This is known as aggregate planning by the company, and helps in setting an ambitious target revenue.
Actual Sales Revenue: Actual sales may be vastly different from forecasted and target sales owing to the changing market complexities. Demand can never be accurately forecasted actually, hence the shortfall. Prices vary over time, discounts are offered, competitive products play important roles in such activities and outcomes. At the end of the time period, the company can compare target revenue versus the actual revenue earned.
All of these help in evaluating the financial position of a company.
Example of Target Revenue
A company selling smartphone has priced it product at $1000.
The company aims to sell 200,000 units in the next financial year.
So the target unit sales = 200,000
Target Revenue= 200,000* $1000 = $200 million
Hence, this concludes the definition of Target Revenue along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team which comprises of MBA students, management professionals, and industry experts. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us