- Business Concepts ›
- Marketing and Strategy ›
- Product Life Cycle (PLC)
Product Life Cycle (PLC)
Definition, Importance & Stages
This article covers meaning & overview of Product Life Cycle (PLC) from marketing perspective.
What is meant by Product Life Cycle (PLC)?
PLC or Product Life Cycle is the journey of any product from its start, growth, maturity & decline. Product life cycle (PLC) deals with the various stages that a product goes through in the market and the business it does. Product life cycle is an important concept in business as it tracks the life cycle of any product, service or brand. PLC represents the performance of sales of a product over a period of time.
Importance of Product Life Cycle (PLC)
Product life cycle is an important concept in business & marketing as it changes a company's strategy. Depending upon the market potential as well as customer demand for a product, every product undergoes a different phase as a part of its product life cycle. The various stages of in the PLC of any product, help a company decide what marketing strategy is to be implemented to ensure maximum return on sales as well as have minimum investment.
Product Life Cycle (PLC) Stages
Product life cycle undergoes broadly 4 different stages i.e.product introduction, product growth, product maturity and then eventually product decline. The stages of PLC can be elaborated as mentioned below:
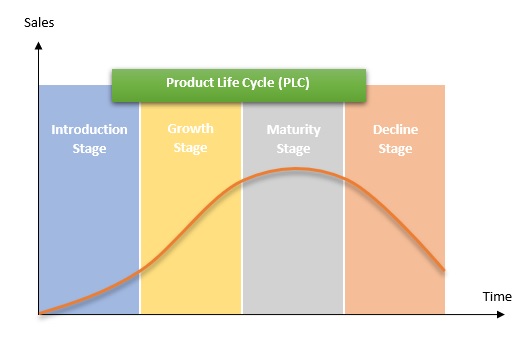
From the above graph, it is clear that sales vary with time and hence the strategies used in each of these stages should be different.
1. Introduction stage – In this PLC stage, sales maybe low and hence the profit would be low. Introduction stage is when a product is introduced in the market. The firm has to engage in heavy promotion to create awareness about the product in the market. Cost plus formula is generally used for determining the price of the product.
2. Growth stage – Sales in this period of product life cycle are rapidly rising and so are the profits. Promotion is not that aggressive in the growth stage. However, firms do offer warranties and other offers to promote the product. The main aim is to increase the market share and sales revenue.
3. Maturity stage – In this PLC stage, sales have reached a peak and even the profits have reached the peak. Here the strategy is to maximize profits and also retain the market share. The firm also tries to price the product in the same range as that of the competitor in the maturity stage. The firm tries to diversify and bring in variations by creating newer models. Thus, strong distribution networks are built and the promotion is increased to create awareness about the new brands.
4. Decline stage –Here, both sales and profits are declining in the decline stage. The strategy is to incur minimal or no expenditure on this product and milk it as much as possible before it declines completely. Hence prices are cut. Promotion is minimized and a strategy of product deletion or product elimination is also considered.
Hence, this concludes the definition of Product Life Cycle (PLC) along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team which comprises of MBA students, management professionals, and industry experts. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us